Big Brain Innovation: Intelligent IT Solutions
Computer Components
What’s inside the box?
Ever wondered what’s inside the box of your computer? The answer isn’t as straightforward as you might expect, due to different people using different terms for the same devices. While using imprecise terminology makes it easier to speak about hardware, it tends to cause confusion when used with people you don’t regularly communicate with. This has led to components having a multitude of names, many of which are not precise. Today, we are going to cover names for the common components inside a computer.
Peripherals
Peripherals are anything that sits outside of and plugs in to the computer case. The core peripherals are keyboard, video monitor, and mouse, often referred to as “KVM”. In most home setups there are speakers as well. Today, it is common to find a plethora of USB devices such as headphones/headsets, microphones, webcams, game pads/joysticks, phone chargers etc.
The Tower
Below is a picture of an assembled computer. To differentiate between the peripherals and the internal components, the computer case (the box) and everything inside of it, is generally referred to as “the tower” based on the original and most popular vertical design.

Personal Computer Tower
Power Supply
The power supply unit, commonly referred to as the PSU, is often overlooked as a computer component, but the computer would not function without it. The PSU is responsible for taking power in from the source (wall outlet), then converting and distributing it appropriately to the individual components within the system. The PSU connects to the motherboard, often via two different cables, as well as to all expansion and storage devices.
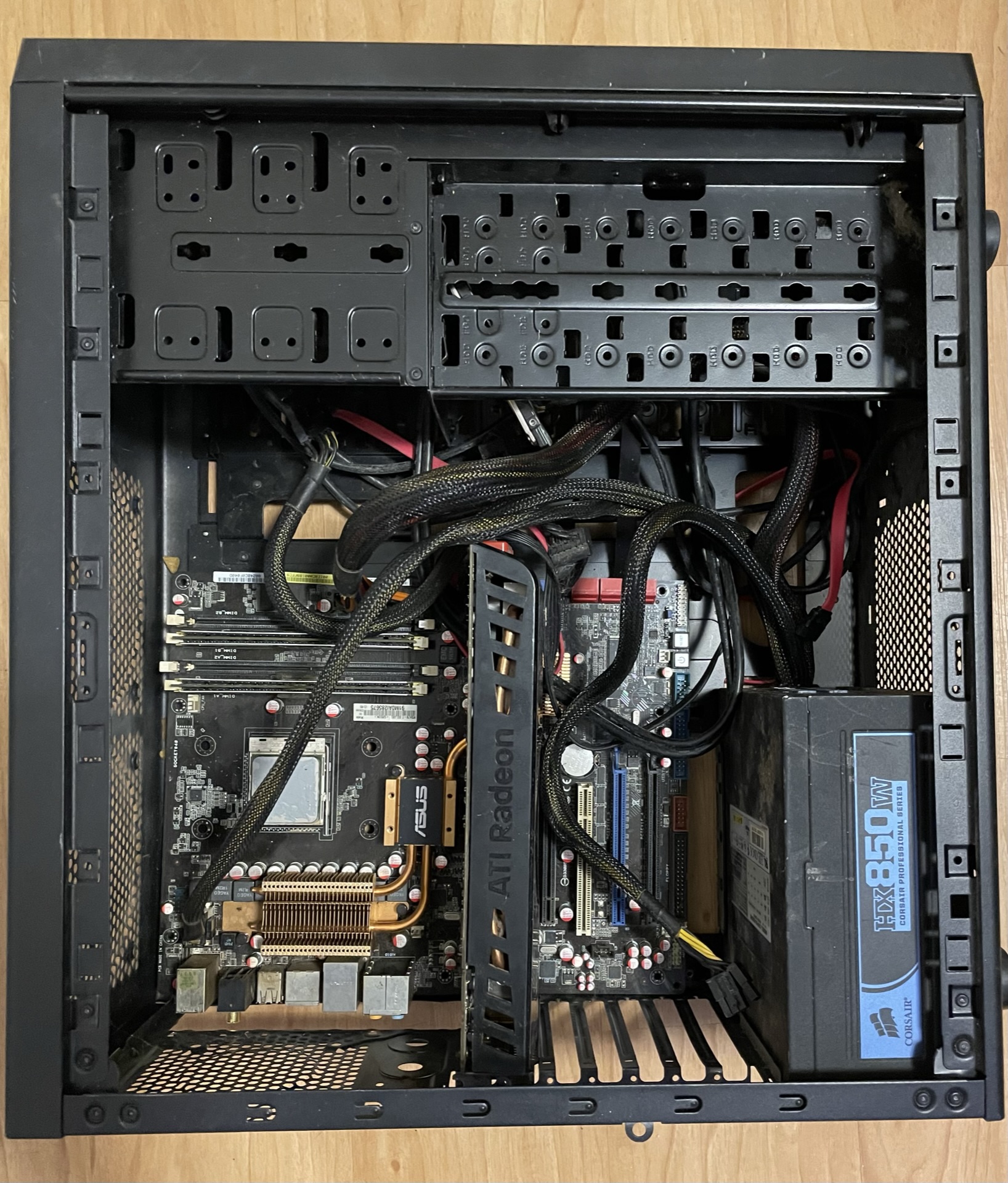
The PSU features a large fan to keep the internal power components cool. It is important to ensure the fan blows out through the casing, not in towards the motherboard and other components. As the PSU is a high-voltage and dangerous device, it is sealed with a “warranty void if removed” sticker. Only electrical engineers should open and work on a PSU as there is a large risk of fire if it is not worked on correctly, so it is replaced as an entire unit. PSUs are measured by the amount of power they can supply across all of the components, in watts. If the wattage of the PSU is insufficient, the components in the PC will not function correctly, if at all.

Power Supply Unit i.e., PSU
Motherboard
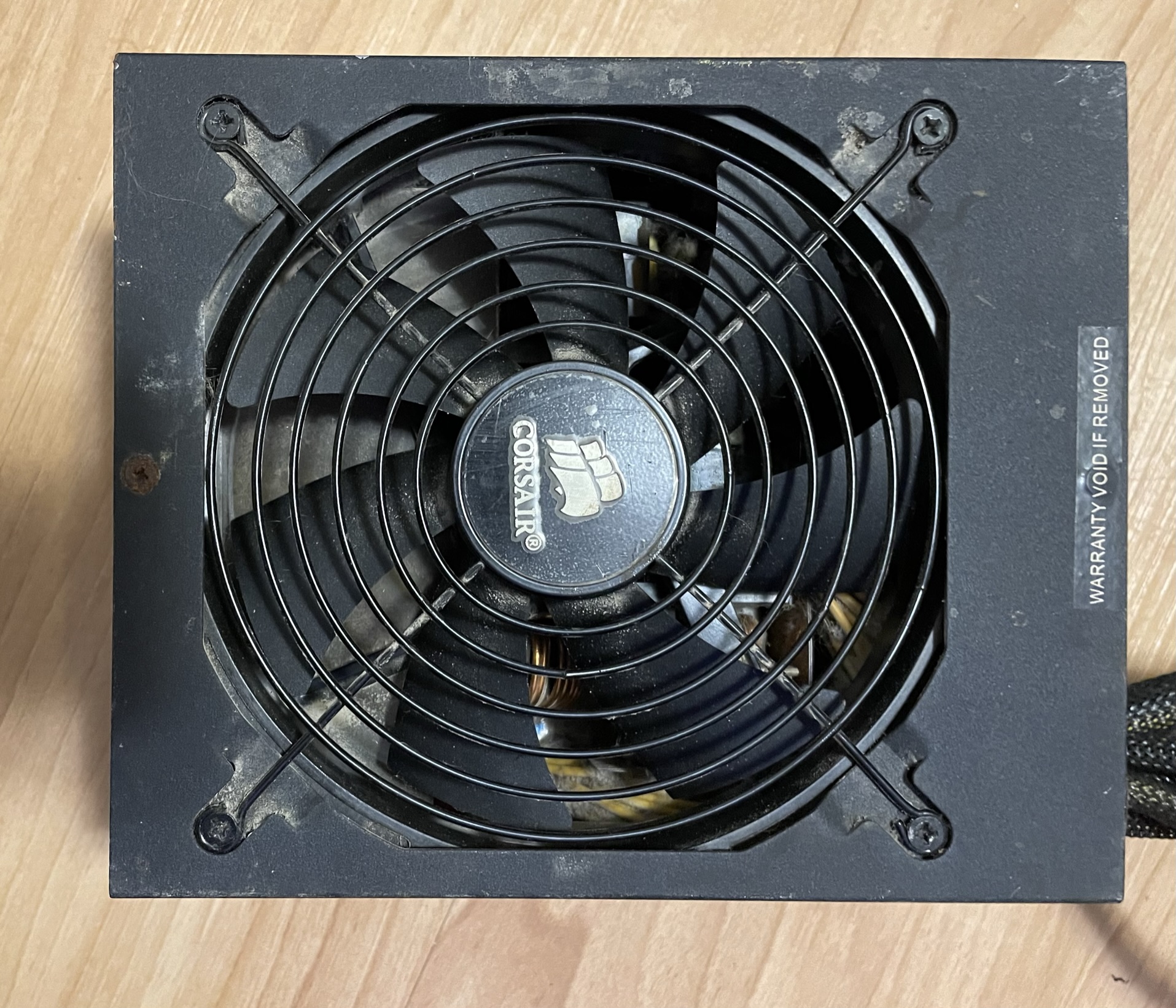
The motherboard, or “mobo” for short, is the largest circuit board in the computer. Its primary responsibility is to provide inter-connectivity for all other components, as well as to power up all the devices correctly via the BIOS settings in the CMOS. The motherboard is more of a routing and distribution system, more than a computational device. Despite this, it is often considered the most crucial device, as no other component will power up correctly or be utilized correctly without it. In extreme situations, a faulty motherboard may cause other devices to be damaged during power up.
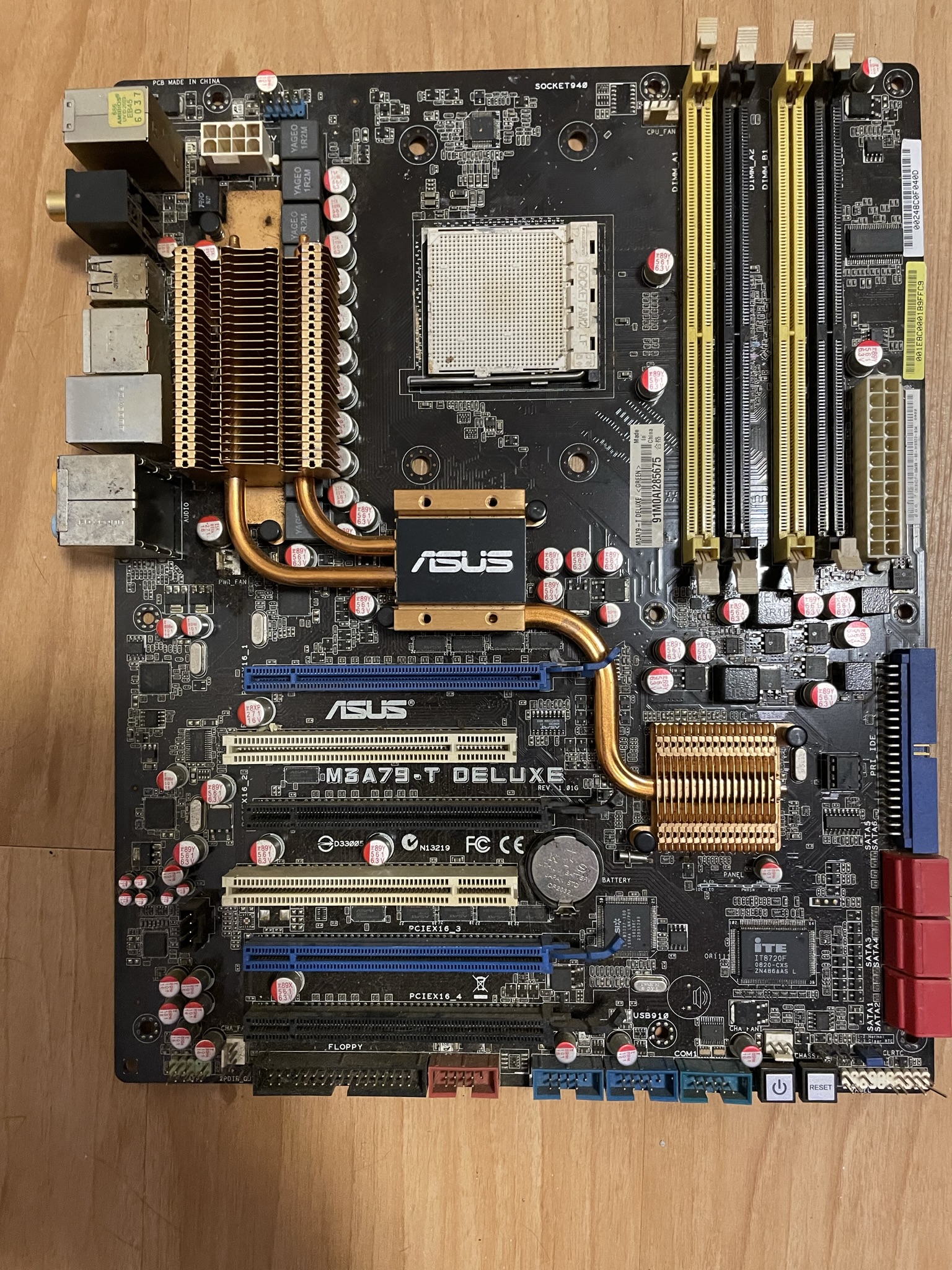
Motherboard
Central Processor
The central processing unit i.e., CPU is the brain (more accurately, the pre-frontal cortex) of the computer. All mathematic computations are done within the CPU. The CPU is the primary device which utilizes micro-electronics, literally electronic circuits created at the microscopic level. Due to the complexity and size of the microelectronics the processors are enclosed in a metallic casing with numerous pins protruding from the bottom to plug in to the motherboard. The density of electronics produces large amounts of heat, so proper sealing and cooling setup is crucial to avoid over-heating, leading to damage and possible fire. These days, thermometers are built in to various parts of the PC which results in turning off power to them before damage is done.
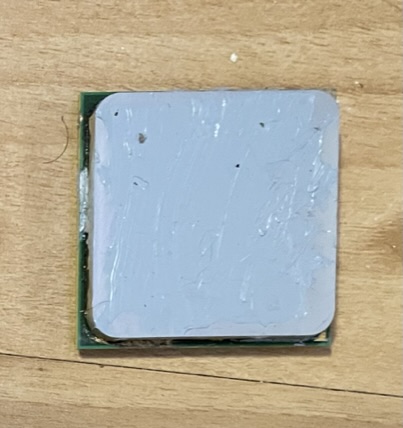
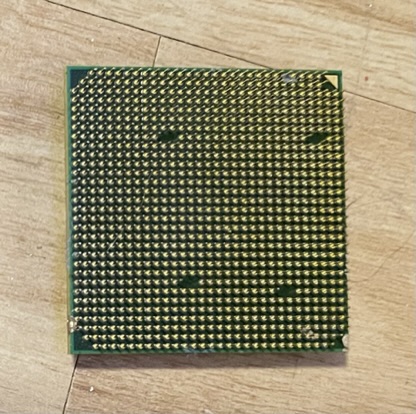


Central Processing Unit - Top and Bottom
RAM
RAM is an acronym which stands for Random Access Memory. RAM is volatile, meaning it is cleared when power is removed. RAM access is extremely fast and operates as the computer’s “working memory”. When RAM fills up, anything which is not needed by the computer to operate in the moment is pushed to a cache on a slower access storage device, such as a hard disk.
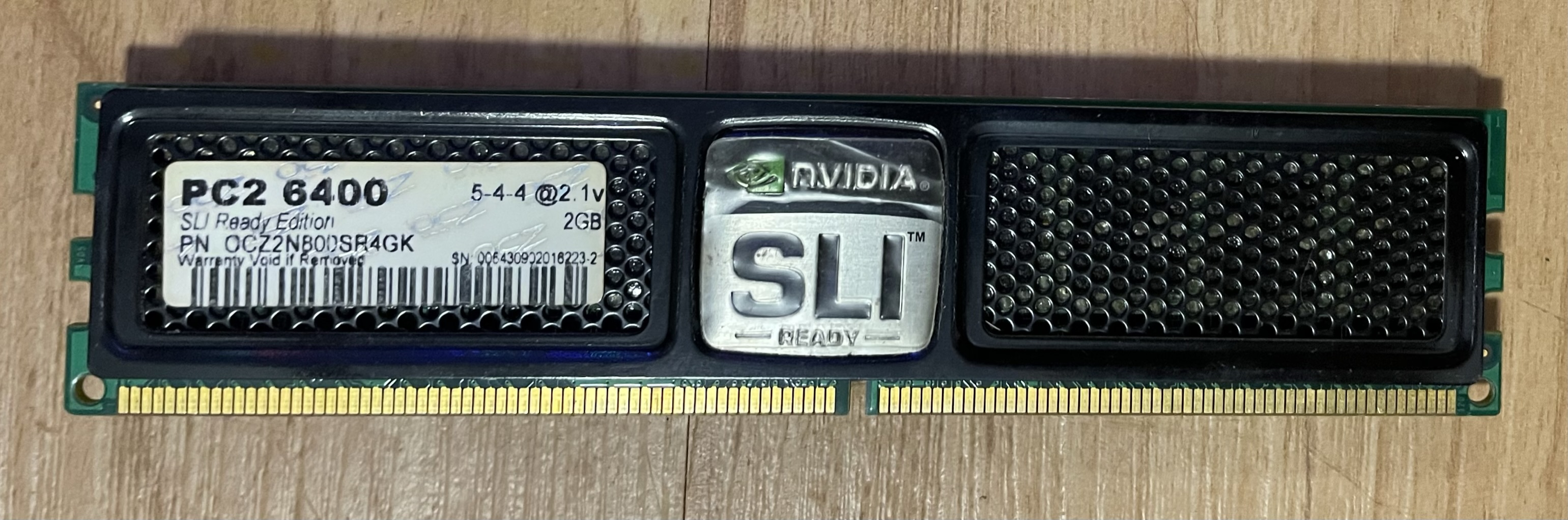

Random Access Memory Module
Hard Disk Drive
Hard drives are non-volatile, meaning they do not clear when power is removed, allowing them act as long-term storage devices. All of your files and data are stored on the hard drive so that they are accessible next time the computer is powered on. Hard drives are also referred to as HDDs or SSDs. Hard drives were originally named to differentiate between drives with hard platters as opposed to the (at the time) more common devices with flexible platters, which were known as floppy disks, or FDDs. Later on the solid disk drive (SSD) was developed, which does not have platters at all, but high density non volatile RAM. High density NVRAM is slower but holds more information than standard RAM.

Small Form Factor Hard Disc
Video Card
The video card, also referred to as the graphics adapter, is responsible for converting instructions in to visible images for display on monitors. Video cards are extremely powerful these days, sometimes costing upwards of $1500. High-end systems often have multiple video cards working in tandem. Most of the work that video cards do is to calculate shading. Shading is a term which encompasses lighting, shadow, and colour differentiation based on light levels.
The extreme computational requirements of calculating shading in real-time requires powerful hardware. Video cards have dedicated processors, referred to as GPUs i.e., graphical processing units. They are very similar to CPUs, though they perform fewer types of calculations in greater numbers. Most high-end systems have more processing resources devoted to video than general use.
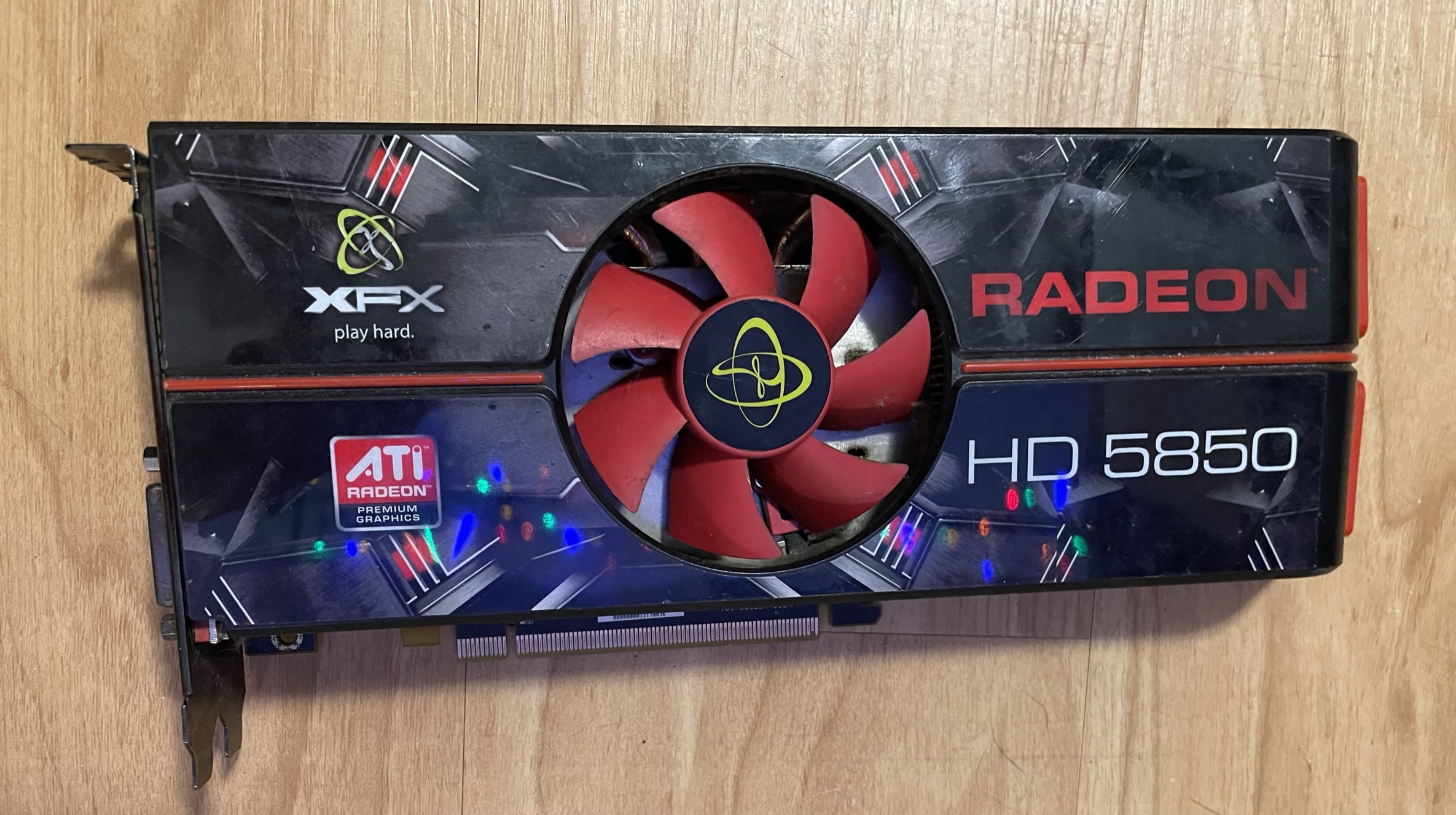

Video Card